How State Charter vs Federal Charter Banking Rules?
How State Charter vs Federal Charter Banking Rules?
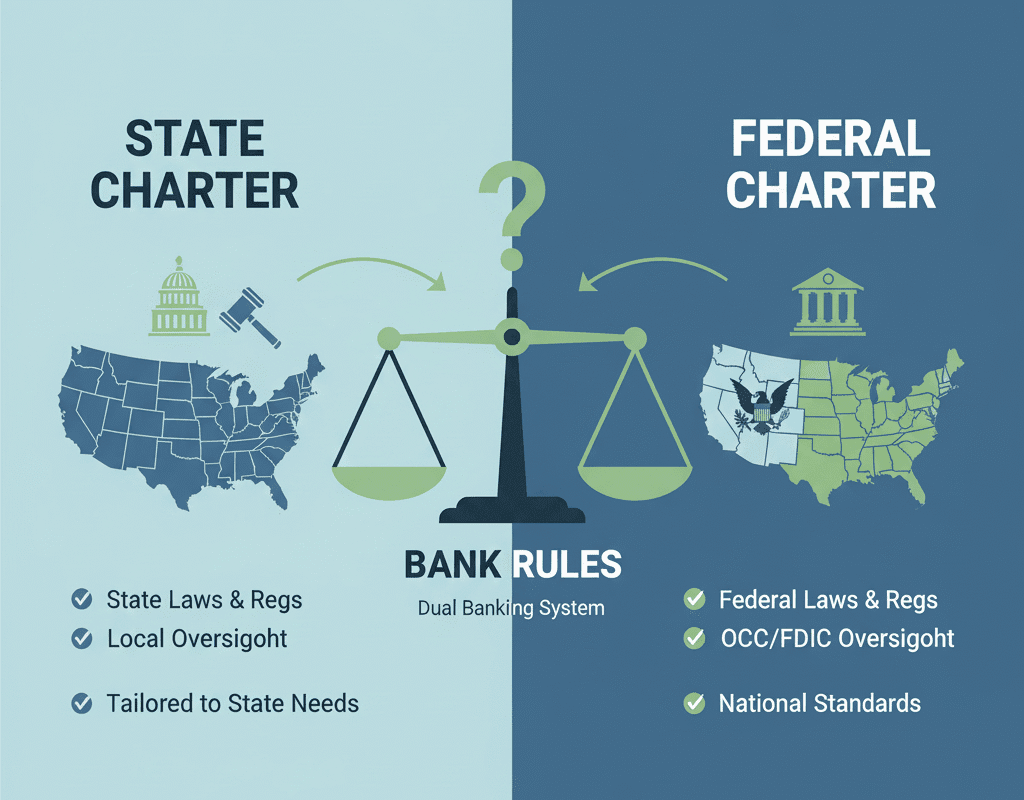
In the United States the banking world is defined by a somewhat unique framework: the so-called dual banking system. Under this structure, banks may operate under a state charter (state-chartered banks) or a federal charter (national banks) — and their choice of charter has significant implications for the rules under which they operate, which regulator they answer to, and how they conduct business.
In 2025, as fintechs, banking innovations, and evolving consumer needs grow, the question of how state-versus-federal charters affect bank rules is increasingly important.
HSBC Cashback Credit Card 2025 – Benefits, Rewards & How to Apply?

Historical context: Why two chartering systems?
The United States banking system has long accommodated both state and federal charters. The “dual banking system” describes this simultaneous existence of state-chartered banks (under state law and state oversight) and federally chartered banks (under federal law and overseen by federal agencies).
The reasons for the dual system include:
- States historically chartered banks and regulated them locally, reflecting local economic and political conditions.
- The federal government established a national banking system (first through the National Banking Acts of the 1860s) to provide uniform rules, national reach and stability.
- Having both systems provides charter choice and dynamism: banks may select a charter based on their business model, geographic reach, regulatory preference and costs.
Charter switching: Why banks move and what happens
Many banks at some point evaluate whether their current charter remains optimal — whether to convert from a state charter to a national charter, or vice-versa. Key reasons include:
- Seeking broader powers or greater interstate reach under a national charter.
- Reacting to state regulatory costs, burdens or perceived disadvantages.
- Seeking more favourable supervisory ratings or regulatory structure.
- Adjusting to changes in law or regulation (e.g., consumer protection rules, chartering trends).
Research shows that banks that changed charters received more favorable supervisory ratings, possibly suggesting that regulators may compete for institutions. But that comes with caveats: banks that switch charters may also have higher risk of failure.
State vs. Federal Charter Benefits and Drawbacks
When assessing charter type, banks (and consequently consumers) should take into account the following:
- Federal (National) Charter Benefits
- Less hodgepodge of state laws and uniform federal regulations throughout states.
- State laws that clash may be preempted by the federal government, particularly in cases of significant interstate activity.
- Possibly more authority, the capacity to “export” interest rates, and the capacity to conduct multi-state operations.
- A federal charter might make regulatory control easier for institutions with national aspirations (single primary regulator).
- Disadvantages of a Federal Charter
- Might face stricter national regulation, higher cost of compliance (depending on size).
- Less flexibility when it comes to tailoring operations to a local or niche market.
- Possible tension with state regulators if the bank’s operations fall under state jurisdiction for certain consumer protection or other laws.
Real-world examples and implications
- A bank operating in just one state, focusing on local community business, may choose a state charter to benefit from local supervision and perhaps lower cost and closer regulator relationship.
- A bank aiming to serve customers across multiple states, engage in nationwide lending, or leverage interest-rate “export” laws may opt for a federal charter to benefit from uniformity and preemption of state laws.
- Fintech companies seeking to become chartered banks face decisions: whether to pursue state charters originally or federal charters, taking into account regulatory burden, geographic scope, cost of compliance, and speed.
- Consumers should recognise that when they deal with a bank, the type of charter may affect the applicable laws and protections — though deposit insurance (through FDIC) is generally common across charter types.
- Regulators and policymakers evaluate how charter choice affects financial stability, competition, consumer protection and innovation. The interplay between state and federal oversight remains essential.
What will change in 2025 and the main areas of risk
Looking ahead to 2025, a number of developments merit consideration:
- Regulatory reform and inspection of the bank charter process: With the rise of fintechs and non-traditional banking entrants, there is increasing pressure to simplify the bank charter process. The approval process and regulatory burden are being examined.
- State versus federal regulatory conflicts: Federal regulators have expressed concern about the fragmentation of the banking sector due to certain state legislation that target bank activities, such as politically sensitive loan choices.
- Regulatory arbitrage risk and charter switching: Concerns regarding safety, consistency, regulatory competitiveness, and financial stability are raised when banks transfer charters to maximize supervision.
In conclusion: How State Charter vs Federal Charter Banking?
For banks in the US, choosing between a state charter and a federal (national) charter is still important. This decision affects regulatory oversight, business model flexibility, geographic reach, risk profile, and consumer protections in addition to being a legal formality.
The charter decision is still on the minds of banking executives, regulators, and policymakers in 2025 as fintechs grow, the regulatory burden increases, state-federal tensions rise, and financial innovation accelerates. Knowing the difference can help customers understand which protections apply and how their banking institution is governed.
How the Federal Budget Process Works in the U.S.: A Complete Guide
How the Federal Budget Process Works in the U.S.: A Complete Guide