Why Unfunded Mandates Strain State Budgets?
Why Unfunded Mandates Strain State Budgets?
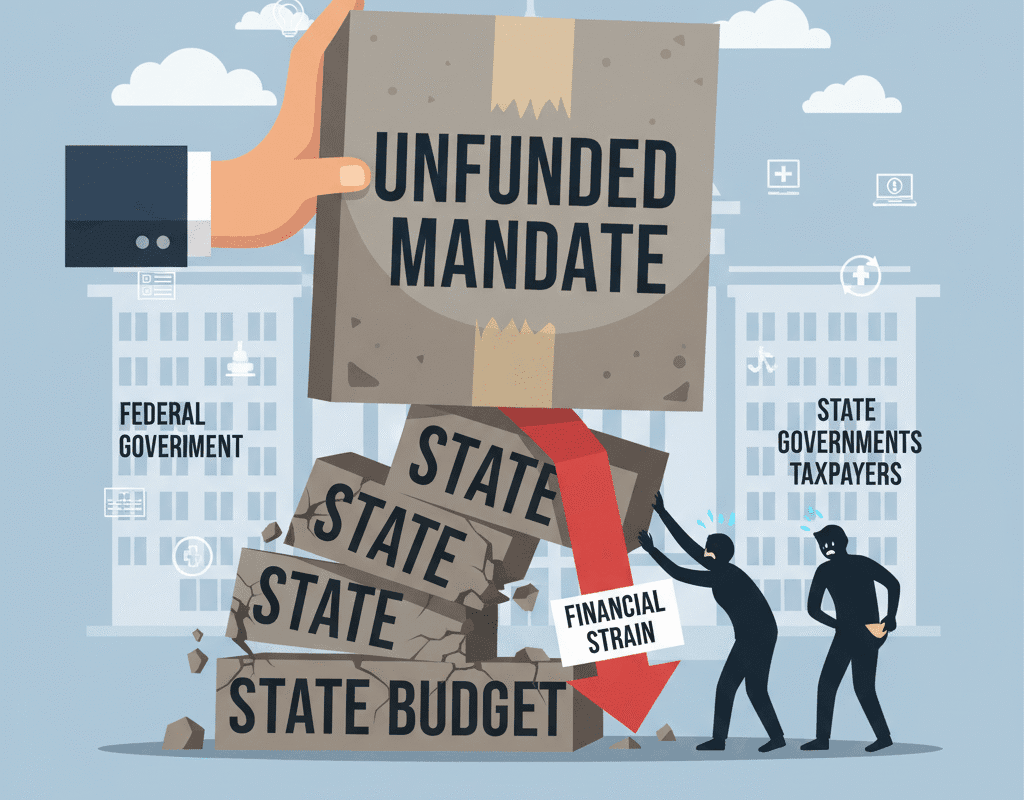
In the US, state governments bear the heavy burden of supplying their inhabitants with basic services, such as public healthcare and education, infrastructure, and social welfare initiatives. However, unfunded requirements remain a major problem for state budgets. These mandates, imposed by the federal government or sometimes other governing bodies, require states to perform certain actions or meet specific standards without providing the necessary funding. As a result, state budgets are placed under tremendous strain, forcing difficult trade-offs and often leading to negative consequences for citizens and public services.
HSBC Cashback Credit Card 2025 – Benefits, Rewards & How to Apply?

Understanding Unfunded Mandates
An unfunded mandate is a law, regulation, or policy directive that requires state or local governments to perform certain functions without providing the funding necessary to cover the associated costs. These mandates can come in various forms, including:
- Federal legislation: Laws passed by Congress that compel states to act in a particular way, such as the Americans with Disabilities Act (ADA).
- Regulatory compliance: Requirements from federal agencies that states enforce, like environmental regulations or public health standards.
- Policy directives: Initiatives that dictate service levels or operational standards, often tied to grants or funding formulas.
Examples of Unfunded Mandates
Several high-profile unfunded mandates have historically put pressure on state budgets:
Education Mandates
Education is one of the most impacted sectors. Federal initiatives, such as the Individuals with Disabilities Education Act (IDEA), require states to provide specific services for students with disabilities. While federal funding is sometimes offered, it rarely covers the full cost, forcing states to supplement the funding to meet legal requirements.
Healthcare Mandates
The Affordable Care Act (ACA) introduced multiple healthcare mandates that affected state budgets. For example, Medicaid expansion required states to provide healthcare coverage to more low-income residents. Although the federal government covered a significant portion initially, states are eventually responsible for a growing share of costs, creating long-term budget pressures.
Consequences for Citizens and Public Services
The ripple effects of unfunded mandates are felt directly by citizens:
- Reduced public services: Budget reallocation can lead to larger class sizes, delayed infrastructure projects, and limited social services.
- Higher taxes: To meet mandates, states may increase taxes or fees, directly impacting household budgets.
- Inequality between states: Wealthier states can better absorb unfunded mandates, while poorer states struggle, creating disparities in service quality across the country.
- Long-term fiscal instability: Persistent reliance on debt or temporary fixes can jeopardize the financial health of state governments, threatening their ability to respond to future crises.
The Federal-State Debate
Unfunded mandates remain a contentious topic in federal-state relations. Proponents argue that they ensure uniform standards, protect vulnerable populations, and promote national priorities. Critics contend that they shift financial responsibility unfairly, reduce state autonomy, and strain public resources. Striking a balance between national goals and state capacity remains a key policy challenge.
Possible Ways to Lessen the Stress
- A number of legislative strategies could lessen the financial burden of unfunded mandates:
- Full or partial federal funding: State budgets are less burdened when federal obligations are accompanied by sufficient financial support.
- Sunset provisions and mandate review: Regularly evaluating mandates and permitting their expiration or modification guarantees their continued applicability and financial viability.
- Increased state flexibility: Reducing expenses while accomplishing policy objectives can be achieved by letting states use different strategies to accomplish goals.
- Impact assessments: To avoid undue financial burden, comprehensive cost-benefit evaluations should be carried out prior to the implementation of mandates.
In conclusion: Why Unfunded Mandates Strain State Budgets?
Unfunded mandates pose a significant challenge to state budgets, compelling governments to make difficult financial decisions, shift resources, and sometimes increase taxes. Even while these regulations’ goals—which range from environmental preservation to healthcare and education—are sometimes well-meaning, the lack of matching funds has serious negative effects on the economy and society.
Addressing this issue requires a coordinated approach that balances federal objectives with state financial realities, emphasizes efficiency and innovation, and ensures equitable access to public services across all states. Without careful management, the strain of unfunded mandates will continue to challenge state budgets, policymakers, and ultimately, the citizens they serve.
The Pivotal Role of the U.S. Chamber of Commerce in Shaping U.S. Public Policy
The Pivotal Role of the U.S. Chamber of Commerce in Shaping U.S. Public Policy