How the Federal Reserve’s Dual Mandate Shapes?
How the Federal Reserve’s Dual Mandate Shapes?
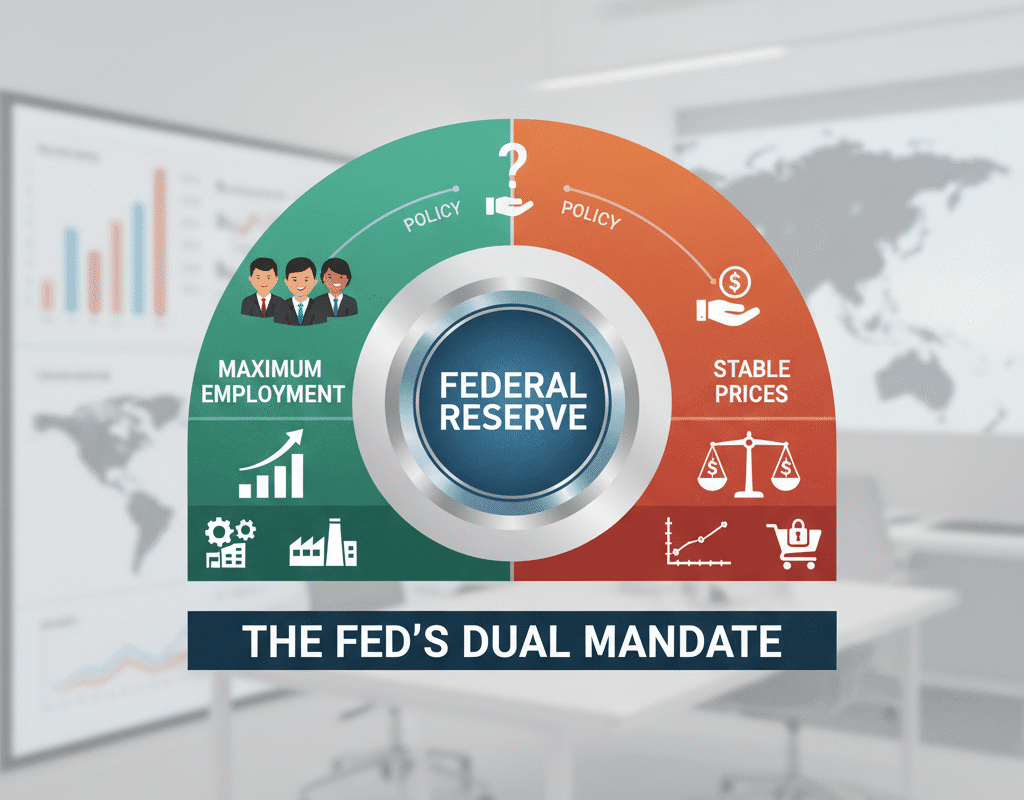
The Federal Reserve, often referred to simply as “the Fed,” is the central bank of the United States. It plays a critical role in shaping the nation’s economic policy, primarily through its dual mandate: promoting maximum employment and ensuring price stability. These twin objectives guide the Federal Reserve’s decisions on interest rates, monetary supply, and broader economic interventions. Understanding the dual mandate is essential for anyone trying to grasp the mechanisms of U.S. monetary policy and its impact on everyday life.
HSBC Cashback Credit Card 2025 – Benefits, Rewards & How to Apply?

The Mandate’s Employment Aspect
Low unemployment rates are only one aspect of maximum employment. The Fed takes into account a number of factors:
- Labor force participation rate: Measures the percentage of working-age people actively participating in the labor market.
- Underemployment: People working part-time who want full-time jobs or those working below their skill level.
- Wage growth: Healthy wages indicate strong demand for workers and a robust labor market.
By monitoring these indicators, the Fed can adjust policy to support employment without letting inflation get out of control.
The Price Stability Side of the Mandate
Stable prices are crucial for economic predictability. Inflation erodes purchasing power, while deflation can stall economic growth. The Fed generally targets a 2% annual inflation rate, considered optimal for balancing growth and price stability.
To achieve this, the Fed monitors:
- Consumer Price Index (CPI): Measures the average price of goods and services purchased by households.
- Personal Consumption Expenditures (PCE) Price Index: Broader than CPI, it reflects changes in consumer spending and is the Fed’s preferred measure of inflation.
- Core inflation: Excludes volatile food and energy prices to give a clearer view of long-term trends.
Maintaining stable prices ensures confidence in the dollar, encouraging investment and economic stability.
Managing Inflation and Employment: Difficulties
The Fed frequently has to tread carefully because of the dual mandate. Rarely can employment and price stability coexist in perfect harmony. Among the difficulties are:
- Stagflation: A rare but dangerous scenario where inflation rises while unemployment remains high. The 1970s oil crisis is a classic example.
- Rapid economic growth: Can reduce unemployment but may trigger inflation, requiring rate hikes that could slow the labor market.
- Recessions: High unemployment and low inflation may push the Fed to lower rates, risking future inflation if recovery is uneven.
Decisions must consider both short-term effects and long-term economic stability. Missteps can have consequences for global markets, consumer confidence, and fiscal policy.
The Role of the Federal Open Market Committee (FOMC)
The FOMC is the Fed’s main policy-making body. It consists of the seven members of the Board of Governors and five regional Federal Reserve Bank presidents. The FOMC meets regularly to:
- Set the target federal funds rate.
- Discuss the current state of the U.S. economy.
- Issue statements and projections to guide markets.
FOMC decisions are closely watched by investors, businesses, and government officials because they shape borrowing costs, investment decisions, and overall economic strategy.
Criticism and Debate Around the Dual Mandate
While widely accepted, the dual mandate is not without controversy:
- Inflation vs. Employment Conflicts: Critics argue the Fed sometimes prioritizes one goal at the expense of the other.
- Market Dependence: Some say markets rely too heavily on Fed interventions, risking long-term economic distortions.
- Global Considerations: In a globalized economy, U.S. Fed policies can affect international trade, currency stability, and foreign economies.
Despite criticisms, most economists agree that the dual mandate provides a clear framework for monetary policy.
In conclusion: How the Federal Reserve’s Dual Mandate Shapes?
A fundamental component of American economic policy is the dual purpose of the Federal Reserve. The Fed plays a crucial role in determining the country’s financial health by aiming for maximum employment and stable pricing. Its tools—interest rates, open market operations, quantitative easing, and forward guidance—allow it to influence economic activity, protect the dollar’s value, and respond to crises.
Understanding the dual mandate not only clarifies why the Fed acts as it does but also underscores the intricate balancing act required to maintain a stable, growing economy. For businesses, investors, and citizens alike, staying informed about Fed policy is essential to navigating the economic landscape.
Why U.S. Tax Breaks for Corporations Spark Political Controversy
Why U.S. Tax Breaks for Corporations Spark Political Controversy