How Roth IRAs Differ from Traditional IRAs?
How Roth IRAs Differ from Traditional IRAs?
The need of prudent retirement planning has never been higher as Americans negotiate an unpredictable economic environment. Individual Retirement Accounts (IRAs) are unique among retirement savings options because of their flexibility and tax benefits.
However, “What’s the difference between a Roth IRA and a Traditional IRA?” is one of the most frequently asked questions by financial advisors.
Although the goal of both accounts is to assist you in saving for retirement, the ways in which they manage taxes, withdrawals, and eligibility can result in quite different financial consequences. Knowing these differences could mean the difference between a retirement that is mostly tax-free and one that is heavily taxed.
We’ll explain the key differences between Roth and Traditional IRAs in this comprehensive analysis, along with which option could be best for your financial objectives.
HSBC Cashback Credit Card 2025 – Benefits, Rewards & How to Apply?

The Basics: What Are IRAs?
Before diving into the differences, it’s important to understand what IRAs are designed to do.
An Individual Retirement Account (IRA) is a type of investment account that offers tax advantages for retirement savings. Unlike 401(k)s, which are employer-sponsored, IRAs are opened and managed individually through financial institutions like banks, brokerages, or investment firms.
The two most common types of IRAs are:
- Traditional IRA
- Roth IRA
Both allow you to contribute a certain amount of money each year, but the timing of your tax benefits is what truly sets them apart.
2025 Contribution Limits
For both Traditional and Roth IRAs, the IRS establishes yearly contribution caps.
The restrictions for the 2025 tax year are:
- $7,000 per year for individuals under age 50
- $8,000 per year for those aged 50 and older (includes a $1,000 catch-up contribution)
However, income limits affect whether you can contribute to a Roth IRA or deduct contributions to a Traditional IRA.
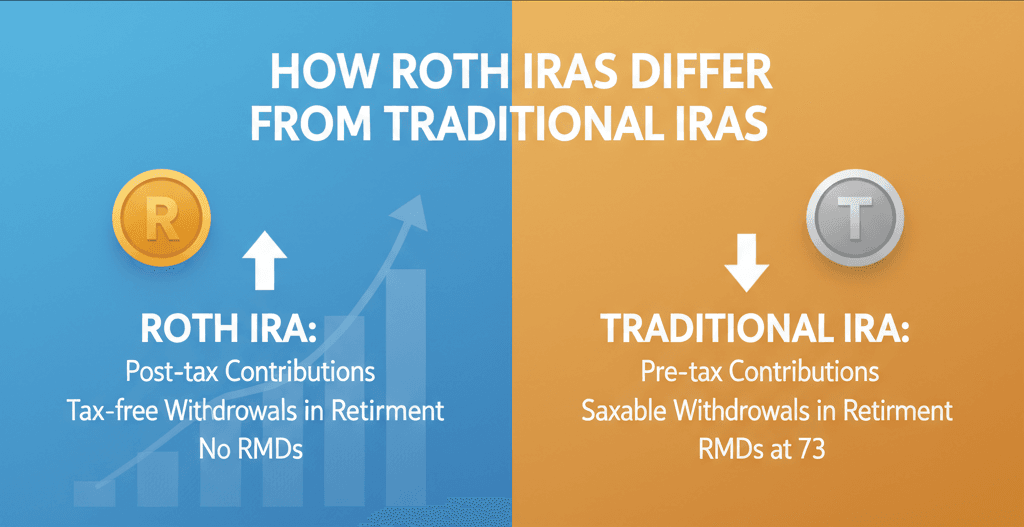
Potential for Long-Term Growth
Both IRAs have the potential for compound growth, but their post-tax values might vary greatly.
Because of tax-deferred compounding, your amount in a Traditional IRA may appear higher. However, a percentage of your final withdrawal is subject to taxes.
You pay taxes up front with a Roth IRA, but you keep all of your retirement withdrawals, including gains.
For many investors, this tax-free compounding makes a Roth IRA particularly appealing, especially for younger savers or those expecting to be in a higher tax bracket in retirement.
Required Minimum Distributions (RMDs)
This is a major differentiator.
- Traditional IRAs: RMDs begin at age 73, per the SECURE 2.0 Act.
- Roth IRAs: No RMDs during your lifetime.
This gives Roth IRA holders more control over their income in retirement — and potentially reduces taxable income, helping to manage Medicare premiums and Social Security taxation.
Conversions: Turning a Traditional IRA into a Roth
You can transfer money from a Traditional IRA to a Roth IRA through a Roth conversion.
You’ll pay taxes on the converted amount now, but future withdrawals will be tax-free.
Conversions can be powerful when:
- You expect future tax rates to rise
- You’re in a temporarily lower income year
- You want to leave tax-free assets to heirs
However, conversions aren’t always beneficial. The upfront tax bill can be substantial, so it’s wise to consult a tax advisor before making the move.
Benefits of Inheritance and Estate Planning
An important benefit for estate planning is offered by Roth IRAs.
You can allow the account to grow unaltered and then transfer it to heirs because withdrawals are tax-free and there are no RMDs throughout your lifetime.
The money must normally be taken out by beneficiaries within ten years, although the withdrawals are still tax-free.
Traditional IRA beneficiaries, on the other hand, will have to pay income tax on withdrawals, which would lower the net inheritance value.
7. Which IRA Is Right for You?
Here’s a quick comparison table summarizing the key differences:
| Feature | Traditional IRA | Roth IRA |
| Tax Treatment | Tax-deductible contributions, taxed withdrawals | After-tax contributions, tax-free withdrawals |
| Income Limits | None for contributions | Income-based contribution limits |
| Withdrawal Rules | Penalty + taxes before 59½ | Contributions always tax-free; earnings tax-free after 59½ and 5 years |
| RMDs | Yes, at age 73 | No RMDs |
| Best For | Those expecting a lower tax rate in retirement | Those expecting a higher tax rate in retirement |
| Estate Benefits | Taxable inheritance | Tax-free inheritance |
Which Will Be More Popular in 2025: Traditional or Roth IRAs?
The popularity of Roth IRAs has increased, according to recent data from retiree surveys and financial organizations.
Younger investors, especially Millennials and Gen Z, are choosing Roth IRAs because they like flexibility and tax-free growth.
A 2025 Fidelity Investments research claims that:
- Roth IRAs accounted for more than 60% of newly established IRA accounts by participants under 35.
- Higher earners who want instant tax deductions continue to favor traditional IRAs.
According to financial advisers, this change indicates a growing need for tax diversification in retirement as well as shifting assumptions regarding future tax rates.
Concluding Remarks: How Roth IRAs Differ from Traditional IRAs?
In the end, both Roth and Traditional IRAs remain cornerstones of retirement planning in 2025.
The right choice depends on your income, age, and future tax expectations.
Financial planners recommend reviewing your IRA strategy annually — especially as tax laws, income levels, and retirement goals evolve.
“It’s not about choosing one over the other,” says James Li, a certified retirement specialist. “It’s about understanding how each tool works and aligning it with your personal financial story.”
With smart planning and informed choices, you can make your retirement savings not just grow — but grow tax-efficiently.
How Federal Income Tax Brackets Work in 2025 – Complete Guide for U.S. Taxpayers
How Federal Income Tax Brackets Work in 2025 – Complete Guide for U.S. Taxpayers